Gradient Descent with momentum or just Momentum is an advanced optimization algorithm that speeds up the optimization of the cost function J. It makes use of the moving average to update the trainable parameters of the neural network. Moving average is the average calculated over n successive values rather than the whole set of values. Mathematically, it is denoted as follow:
\[ A_{t}=\beta A_{t-1}+(1-\beta) X_{t} \]
Here, A[i] represents the moving average at the i data point for the value X[i]. The parameter β controls the value n over which average is calculated. While training a neural network, the goal is to optimize the cost function J and minimize its value. A traditional gradient descent optimizer follows the blue path, whereas the momentum optimizer follows the green path to reach the minimum.
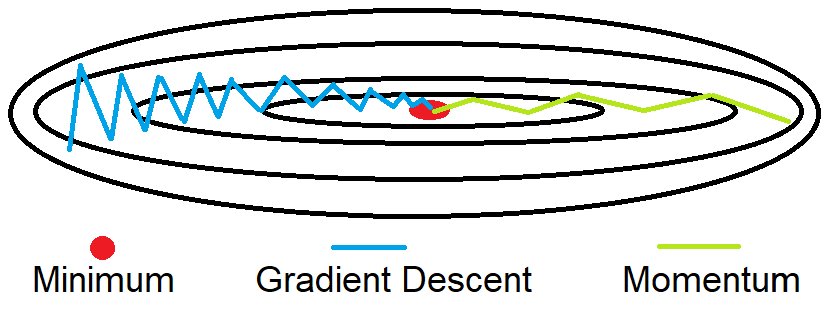
As we can see from the figure above, we want to minimize the oscillation on the y-axis, and on the x-axis we want faster learning. The momentum smooth out the steps of gradient descent as represented by the green oscillation of the figure above. It represent the velocity to reach the minimum and has two hyperparameters: 1 - the learning rate alpha 2 - the parameter beta that control the exponentially weighted average. The most common parameter for beta is 0.9 which appears to be a very robust value.
Reference: coursera deep neural network course